Direct and Indirect Speech in Hindi | Narration
Direct and Indirect speech को Narration भी कहा जाता है, हिंदी में इसे प्रत्यक्ष और अप्रत्यक्ष कथन कहते हैं। Narration में वाक्यों को दो प्रकार से कहा या लिखा जा सकता है। एक तो जैसा कहा गया है, सीधा (direct) उसी शब्द को दोहरा दिया जाये। दूसरा, वाक्य का अर्थ वही रहे लेकिन बोलने या लिखने के दौरान इसे अपने शब्दों में अलग तरीके से (indirect) कहा जाये। इसकी परिभाषा निम्नलिखित है।
- Direct Speech -- किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कहे गए बातों को उसी के शब्दों में दोहराया जाता है तो यह Direct Speech कहलाता है।
- Indirect Speech -- किसी व्यक्ति द्वारा कहे गए बातों को उसी के शब्दों में न दोहराकर उसके अर्थ को अपने शब्दों कहा जाये तो यह Indirect Speech कहलाता है।
ध्यान दें की direct and indirect speech के साथ speech शब्द है जिसका अर्थ है, भाषण या कथन। Speech शब्द इस बात को दर्शाता है की कोई बात किस के द्वारा कहा गया, इसलिए English grammar के इस टॉपिक के अंतर्गत उन वाक्यों का अनुवाद सीखेंगे जो किसी के द्वारा कहा गया हो, न की लिखा गया हो।
पहचान
Direct speech को पहचानने का सबसे आसान तरीका है quotation marks या inverted commas, जब भी कोई वाक्य direct speech में होता है तो वाक्य के एक हिस्से को inverted commas के अन्दर लिखा जाता है। Indirect speech में inverted commas का लोप हो जाता है और इसके बदले हिंदी में "कि" या अंग्रेजी में "that" शब्द का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
Interrogative वाक्यों में ask और if का प्रयोग किया जाता है जिसे हमलोग आगे विस्तार से समझेंगे।
Direct Speech Example
- उसने मुझसे पुछा, "तुम कहाँ रहते हो?"
- He asked me, "Where do you live?"
- उसने कहा, "मैं जा रहा हूँ।"
- He said, "I am going."
Indirect Speech Example
- उसने मुझसे पुछा कि मैं कहाँ रहता था?
- He asked me Where I lived?
- उसने कहा कि वह जा रहा था।
- He said that he was going.
Use of Reporting Verbs
किसी दुसरे द्वारा कहे गए कथन को जब आप उसी शब्द में दोहरायेंगे तो सुनने वाले को लगेगा, यह आपके ही शब्द हैं। ऐसे में अपनी बात को स्पष्ट रूप से कहने के लिए हमलोग "reporter" और "reporting verbs" का प्रयोग करते हैं। इनका प्रयोग वक्ता के कथन से पहले या बाद में किया जाता है। जैसे- उसने कहा, मैंने पूछा, मामा जी ने सुझाव दिया, राम ने जवाब दिया इत्यादि। इन वाक्यांशो में उसने, मैंने, मामा, राम इत्यादि reporter कहलायेंगे।
नोट : Reporting verb के बाद वाले भाग को reporting speech कहा जाता है।
नीचे reporting verbs की सूची, उनके अर्थ के साथ दी गयी है। दिए गए सभी verb past participle (V3) form हैं।
| Reporting Verbs |
|---|
| Said - कहा (सामान्य वार्तालाप के लिए) |
| Told: कहा (information, facts, or ideas बताने के लिए) |
| Asked: पूछा (किसी चीज़ के बारे में जानकारी के लिए) |
| Admitted: स्वीकार किया (किसी बात को स्वीकार करना या मान लेना) |
| Suggested: सुझाव दिया |
| Exclaimed: जोर से बोलना (emotion में) |
| Replied: जवाब दिया |
| Explained: विस्तारपुर्वक बताया |
| Stated: स्पष्टता से कहा |
| Warned: चेतावनी दिया |
|
Asserted: आत्मविश्वास से कहा
|
|
Inquired: पूछा (जानकारी लेने के उद्देश्य से पुछताछ)
|
| Suggested: सुझाव दिया |
|
Revealed: उजागर किया
|
|
Agreed: सहमत हुआ
|
|
Denied: इंकार किया
|
|
Complained: शिकायत किया
|
|
Mentioned: उल्लेख किया
|
|
Insisted: हठपूर्वक आग्रह किया
|
|
Announced: घोषणा किया
|
|
Confirmed: निश्चित किया
|
|
Reported: रिपोर्ट किया
|
|
Recalled: याद आया (भूलने के पश्चात किसी चीज़ का दुबारा याद
आना)
|
Direct और Indirect Speech में अंतर
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
|
वक्ता के कथन को हुबहू उसी के शब्दों में Quotation marks (" ") के अन्दर लिखा जाता है। उदाहरण: उसने कहा, "मैं जा रहा हूँ।" (He said, "I am going.") |
वक्ता द्वारा कहे गए कथन के अर्थ को अपने शब्दों में कहा जाता है। उदाहरण: उसने कहा कि वह जा रहा था। (He said that he was going.) |
|
Direct speech के वाक्यों में वक्ता द्वारा कहे गए सर्वनाम शब्द (Pronoun) में कोई बदलाव नहीं होता है। उदाहरण: उसने कहा, "मैं जा रही हूँ।" (She said, "I am going.") |
Indirect speech के वाक्यों में वक्ता द्वारा कहे गए सर्वनाम शब्द (Pronoun) को बदला जाता है।
उदाहरण: उसने कहा कि वह जा रही थी। (She said that she was
going.)
|
| Direct Speech में कथन को जैसा कहा गया हो वैसा ही लिखा जाता है और इसके tense में कोई बदलाव नहीं होता है। | Indirect Speech में tense को कथन और इसके दोबारा बोलने के समय अनुसार बदला जाता है। |
| Direct Speech में reporting verb को कथन के बाद भी लगाया जा सकता है। | Indirect Speech में reporting verb को कथन के पहले ही लगाना होता है। |
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples in Hindi
नीचे direct and indirect speech के कुछ उदाहरण दिए गए हैं, इन उदाहरणों को ध्यान से पढ़े और समझे। इसके बाद हमलोग यह देखेंगे की direct से indirect speech में बदलने के दौरान person और tense में क्या परिवर्तन आते हैं।
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
रमेश ने कहा, "मैं अकेला हूँ।"
|
रमेश ने कहा कि वह अकेला था।
|
अब निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को देखिये:
|
उसने कहा He said |
उसने मुझसे कहा He said to me |
|
माँ ने पुछा Mother asked |
माँ ने मुझसे पूछा Mother asked me |
|
रमेश ने कहा Ramesh told |
रमेश ने मुझसे कहा Ramesh told me |
|
उसने जवाब दिया He replied |
उसने पूजा को जवाब दिया He replied to Puja |
|
मेरा भाई कहता है My brother says |
मेरा भाई मुझसे कहता है My brother says to me |
|
उसने वादा किया He promised |
उसने मुझसे वादा किया He promised to me |
दिए गए उदाहरणों में आपने देखा की कुछ वाक्यों में to का प्रयोग हुआ है और कुछ में नहीं। इनका प्रयोग transitive और intransitive verb के ऊपर निर्भर करता है। जिसमे केवल transitive verb के साथ ही to का प्रयोग होगा।
यदि आप साधारण भाषा में समझना चाहते है तो नीचे उन reporting verb की list दी गयी है, जिसके बाद to का प्रयोग किया जाता है। ध्यान रहे की to के बाद एक object का होना आवश्यक है। नीचे दिए गए reporting verbs को छोड़कर अन्य जितने भी reporting verb हैं उनके साथ सामान्यतः to का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता है।
| Verb | Examples |
|---|---|
| Say | He said to me, "I'll be there." |
| Speak | She spoke to him about her plans. |
|
Explain
|
They explained to us how it works. |
|
Recommend
|
He recommended to her a good book to read. |
|
Suggest
|
She suggested to him a new idea. |
|
Offer
|
She offered to me some advice. |
|
Promise
|
He promised to her that he would come. |
|
Propose
|
He proposed to us a solution. |
|
Apologize
|
She apologized to him for being late. |
|
Reply
|
He replied to her with a smile. |
|
Declare
|
She declared to him her intentions. |
|
Deny
|
He denied to her any involvement. |
|
Express
|
She expressed to him her concerns. |
|
Object
|
He objected to her proposal. |
|
Acknowledge
|
He acknowledged to her his mistake. |
|
Claim
|
She claimed to him that she saw the accident. |
|
Confess
|
He confessed to her his love. |
|
Complain
|
She complained to him about the noise. |
|
Object
|
He objected to her proposal. |
|
React
|
She reacted to him with surprise. |
|
Report
|
They reported to us the news. |
Note : यदि direct speech के reporting verb में say/says/said के बाद कोई object रहे तो indirect speech में इसे tell/tells/told में बदल दिया जाता है और tell/tells/told के बाद to का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता है।
Direct & Indirect Speech (Narration) Rules in Hindi
Direct & indirect speech में आपको person और tense में होने वाले बदलाव को समझना है। यदि reporting verb past tense (V3) में हो तभी टेंस में बदलाव किया जाता है। अगर reporting verb present tense या future tense में रहे तो टेंस में कोई बदलाव नहीं होगा, लेकिन person में बदलाव सभी प्रकार के वाक्यों में होता है।
कुछ शब्दों का direct speech में तात्पर्य अलग होता है अगर हम उन शब्दों को वैसा ही indirect speech में प्रयोग करते हैं तो इनके गलत अर्थ निकल सकते हैं। जैसे मान लीजिए आप परसों अपने दोस्त को कहते हैं की मैं कल दिल्ली गया था। इसका अर्थ है की आप परसों से एक दिन पहले दिल्ली गए थे।
अगर कोई आज आपकी बात को indirect speech में कहे कि वह कल दिल्ली गया था तो ऐसा प्रतीत होगा की कल ही की बात हो रही है। इसलिए इन शब्दों को बदलना अनिवार्य हो जाता है। नीचे उन शब्दों की सारणी दी गयी है।
| Direct Speech | Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| This | That |
| These | Those |
| Here | There |
| Hence | Thence |
| Now | Then |
| Thus | So |
| Today | That day |
| Yesterday | The previous day |
| Tomorrow | The following day |
Change of Person in Indirect Speech
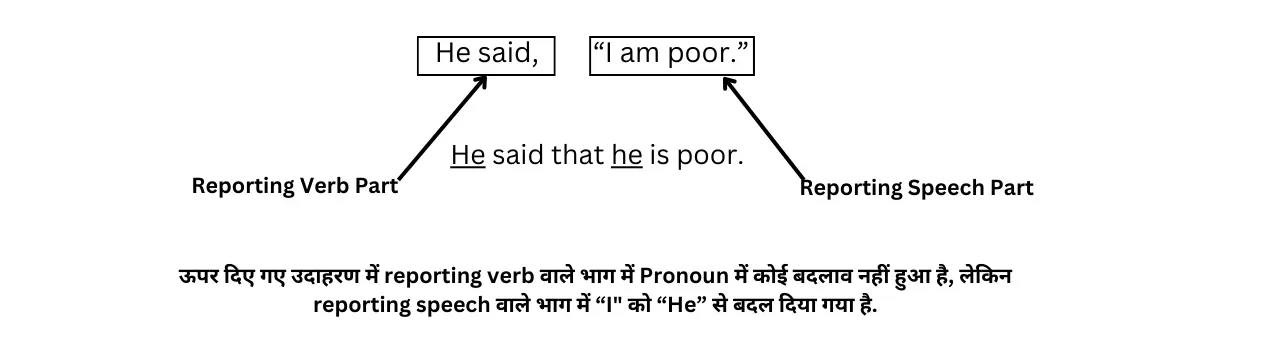
सबसे पहले यह समझिये कि direct speech दो भाग में होता है, एक भाग में reporting verb होता है और दुसरे भाग में reporting speech, जब भी हम person या pronoun में बदलाव करेंगे तो reporting speech वाले भाग में करेंगे। Reporting verb में जो person या pronoun शब्द होता है उसे कभी भी बदला नहीं जाता है।
यदि reporting speech का subject third person में रहे तो indirect speech के उस subject में कोई बदलाव नहीं किया जाता है। Person में परिवर्तन केवल तीन सर्वनाम (I/we/you) के साथ होता है जिसे हमलोग आगे समझेंगे।
Rule 1: यदि Direct speech के reporting speech part में subject I/we हो तो Indirect Speech में इसे reporting verb के subject के अनुसार change किया जाता है। नीचे दिए गए चित्र को देखें।
Examples:-
- They said, "We can live here."
- They said that they could live there.
- She said, "I am happy."
- She said that she is happy.
- Mohan and Sohan said, "We are in trouble."
- Mohan and Sohan said that they were in trouble.
Rule 2 : यदि Direct speech के reporting speech का subject "you" रहे तो इसे reporting verb के object के अनुसार बदला जाता है। जैसे:-
| Object | Subject |
|---|---|
| Me | I |
| Us | We |
| You | You |
| Him | He |
| Her | She |
| Them | They |
| Name (Puja, Ramesh, Mohan, Raju) | He or She (According to gender) |
Examples:-
- He said to me, "you are useless."
- He told me that I am useless."
- Mohan blamed us, "you are guilty."
- Mohan blamed us that we were guilty.
- They said to you, "you are clever."
- They told you that you are clever.
- Father said to him, "you are lazy."
- Father told him that he is lazy.
- Brother said to her little sister, "you are cute."
- Brother told her little sister that she is cute.
- The teacher reacted to them, "you are cheater."
- The teacher reacted to them that they are cheater.
- I said to Raju, "you are older than me."
- I told Raju the he is older than me.
- Raju said to Puja, "you are younger than me."
- Raju told Puja that she is younger him.
Change of Tense in Indirect Speech
यदि reporting verb प्रेजेंट या फ्यूचर टेंस में रहे तो indirect speech में टेंस से संबंधित कोई भी बदलाव नहीं किया जाता है लेकिन reporting verb past टेंस में रहे तो indirect speech के reported speech में निम्न सारणी के अनुसार बदला जाता है।
| Tense of Direct Speech | Tense of Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| Present Indefinite Tense | Past Indefinite Tense |
| Present Continuous Tense | Past Continuous Tense |
| Present Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Tense |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Past Indefinite Tense | Past Perfect Tense |
| Past Continuous Tense | Past Perfect Continuous Tense |
| Past Perfect Tense | No change |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | No Change |
आपने ध्यान दिया होगा कि उपर दिए गए टेबल में future टेंस का उल्लेख नहीं किया गया है। ऐसा इसलिए क्योंकि future tense को helping verb के अनुसार बदला जाता है। Future tense का structure वही रहेगा केवल shall/will को should/would से बदल दिया जाता है।
नीचे कुछ helping verb को दर्शाया गया है, जिन्हें देखकर आप समझ सकते हैं की direct and indirect speech में इनके रूप किस प्रकार परिवर्तित होते हैं।
| Helping verb: Direct Speech | Helping verb: Indirect Speech |
|---|---|
| Is/Am/Are | Was/Were |
| Was/Were | Had been |
| Shall/Will | Should/Would |
| Have/Has | Had |
| Had | Had had or Had |
| Can | Could |
| May | Might |
अपने विवेक का प्रयोग करें
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों पर विचार करें -
- उसने कहा, "मैं एक डॉक्टर हूँ।"
- He said, "I am a doctor."
- उसने कहा की वह एक डॉक्टर है।
- He said that he is a doctor.
ऊपर दिए गए उदाहरण में indirect speech को past टेंस में नहीं बदला गया है। क्योंकि वह अभी भी एक डॉक्टर है। अगर ऐसा कहा जाये, He said that he was a doctor, तो इसका अर्थ होगा वह डॉक्टर था, अभी नहीं है।
- मैंने पूछा, "आप क्यों दौड़ रहे हैं?"
- I asked, "why are you running?"
- मैंने पूछा कि वह क्यों दौड़ रहा था।
- I asked that why was he running.
इस वाक्य में was का प्रयोग किया गया है जो दर्शाता है की दौड़ने का कार्य past में ही समाप्त हो गया होगा। अगर हम यहाँ "is" का प्रयोग करते तो इसका अर्थ होता की वह तब से लेकर अभी तक दौड़ ही रहा है। इसलिए यहाँ पर टेंस को बदलना आवश्यक था।
- शिक्षक ने कहा, "जीवन के लिए पानी आवश्यक है।"
- The teacher said, "water is essential for life."
- शिक्षक ने कहा कि जीवन के लिए पानी आवश्यक है।
- The teacher said that water is essential for life.
वाक्य में पानी का जीवन के लिए आवश्यक होना एक universal truth है, इसलिए tense में कोई बदलाव नहीं किया गया है। यह वाक्य भूत, भविष्य, वर्तमान सभी समय के लिए सत्य है।
इन उदाहरणों का उद्देश्य यह समझाना है की आपको हर जगह tense को नहीं बदलना चाहिए, वाक्य के प्रसंग को समझे फिर उसका अनुवाद करें।
Direct and Indirect Speech Examples
- उसने कहा "मैं वहां गया था।"
- He said, "I went there."
- He said that he had gone there.
- लड़कों ने कहा "हमलोग खेलने जा रहे हैं।"
- The boys said, "We are going to play."
- The boys said that they were going to play.
- माँ ने कहा, "मैं बीमार नहीं हूँ।"
- Mother said, "I am not ill."
- Mother said that she was not ill.
- पिताजी ने कहा, "कुछ करो, फालतू मत बैठो।"
- Father said, "Do something, don't sit idle."
- Father said to do something and not to sit idle. (reporting speech में subject न हो तो that को हटा कर to का प्रयोग)
- नेहा ने कहा, "मैं घर का काम करती हूँ।"
- Neha said, "I do household work."
- Neha said that she did household work.
- राहुल ने कहा, "मैं नहा रहा हूँ।"
- Rahul said, "I am bathing."
- Rahul said that he was bathing.
- मनोज ने कहा, " मैं खा चूका हूँ।"
- Manoj said, "I have eaten."
- Manoj said that he had eaten.
- वह कहता है, "मैं तुम्हारा मित्र हूँ।"
- He says, "I am your friend."
- He says that he is my friend. (Reporting verb अगर प्रेजेंट में हो तो टेंस नहीं बदलता है)
- मोदी जी कहते हैं, "हमलोग ईमानदार हैं।"
- Modi ji says, "we are honest."
- Modi ji says that they are honest.
- राहुल जी कहते हैं, "वे लोग बेईमान हैं।"
- Rahul ji says, "they are dishonest."
- Rahul ji says that they are dishonest. (third person subject में कोई बदलाव नहीं होगा)
- वह कहती है, "मैं एक गायिका हूँ।"
- She says, "I was a singer."
- She says that she was a singer. (again reporting verb अगर present/future में रहे तो reporting speech का टेंस नहीं बदलता है)
- स्टेशन मास्टर ने कहा, "ट्रेन जा चुकी है।"
- Station master said, "the train has left."
- Station master said that the train had left. (present perfect tense से past perfect tense)
- रामू ने कहा, "उसने नहीं पीटा।"
- Ramu said, "he didn't beat."
- Ramu said that he had not beaten. (simple past से past perfect tense)
- भाभी ने कहा, "कुछ खा लो।"
- Bhabhi said, "have some food."
- Bhabhi said to had some food. (reporting speech में subject न हो तो that को हटा कर to का प्रयोग)
- पिताजी ने कहा, "इसे खाना मत दो।"
- Father said, "don't feed him."
- Father said not to feed him. (negative वाक्य में subject न हो तो that के बदले not का प्रयोग करें)
- लोगो ने कहा, "तुम खिलाडी हो।"
- People said, "You are a player."
- People said that I am a player. (again common sense वाली बात, खिलाडी होना एक talent है जो आज भी हो सकती है)
- वह कहेगी, "मुझे माफ़ कर दो।"
- She will say, "Forgive me."
- She will say to forget her.
- विजय कहता है, "मैं अमीर बनूँगा।"
- Vijay says, "I shall be rich."
- Vijay says that he will be rich.
- अजय कहता है, "तुम गरीब रहोगे।"
- Ajay says, "You will be poor."
- Ajay says that I shall be poor.
- मैं कहता हूँ, "दोनों गलत हैं।"
- I say, "Both are wrong."
- I say that both are wrong.
- सीमा ने कहा, "वह पढ़ चुकी थी।"
- Seema said, "She had read."
- Seema said that she had read. (Past perfect tense, no change)
- उसने कहा, "मैंने आपको कहीं देखा है।"
- He said, "I have seen you somewhere."
- He said that he had seen me somewhere.
- उसने कहा, "यह अच्छी जगह नहीं है।"
- He said, "This is not a good place."
- He said that that was not a good place.
- राजू ने कहा, "मैं इस स्कूल में नहीं पढूंगा।"
- Raju said, "I will not study in this school."
- Raju said that he would not study in that school.
- उसने बोला, "राजा को रानी से प्यार हो गया।"
- He said, "The King has fallen in love with the Queen."
- He said that the King had fallen in love with the Queen.
- मास्टर जी ने कहा, "तुम शराब पीते हो।"
- Master ji said, "You drink."
- Master ji said that I drank. (simple present to simple past)
- उसने कहा, "मेरा दोस्त यहाँ पढता है।"
- He said, "My friend studies here."
- He said that his friend studied there.
- पंकज ने कहा, "मैं कल मुंबई जाऊंगा।"
- Pankaj said, "I shall go to Mumbai tomorrow."
- Pankaj said that he would go to Mumbai the following day.
- श्रुति ने कहा, "मैं अगले महीने जाऊँगी।"
- Shruti said, "I shall go next month."
- Shruti said that she would go the following month.
- अंजलि ने कहा, "मैं अकेले जा सकती हूँ।"
- Anjali said, "I can go alone."
- Anjali said that she could go alone.
Interrogative Sentences of Indirect Speech
Interrogative sentence के indirect speech में inverted commas के बदले that का प्रयोग नहीं होता है। ऐसे में reporting verb में ask का प्रयोग करें और reporting speech को question word से शुरू करें। Question word के बाद वाक्य को affirmative में बदल दें। Tense में होने वाले बदलाव की तालिका ऊपर पहले ही दे दी गयी है।
- उसने कहा, "तुम कब सोते हो?"
- He said, "When do you sleep?"
- He asked when I slept.
- उसने कहा, "अजय क्या कर रहा है?"
- He said, "What is Ajay doing?"
- He asked what Ajay was doing.
- मैंने कहा, "तुमने यह कैसे किया है?"
- I said, "How have you done this?"
- I asked how he had done that.
- नेहा ने कहा, "वह कैसे दो दिन से मेरी मदद कर रहा है?
- Neha said, "How has he been helping me for two days?"
- Neha asked how he had been helping her for two days.
- राम ने पुछा, "तुम कहाँ गए थे?"
- Ram said, "Where did you go?"
- Ram asked where he had gone.
- माँ ने कहा, "तुम क्यों खेल रहे थे?"
- Mother said, "Why were you playing?"
- Mother asked why I have been playing.
- दिनेश ने पूछा, "तुम कब पढ़ चुके थे?
- Dinesh asked, "When had you study?
- Dinesh asked when I had studied.
- दीदी ने पूछा, "वह दो पांच दिन से कहाँ रह रहा था?"
- Sister asked, "Where had he been living for five days?"
- Sister asked where he had been living for five days.
- उसने पूछा, "तुम्हे कैसे पता चलेगा?"
- He asked, "How will you know?"
- He asked how I would know.
- रमेश ने पूछा, "वह कहाँ पढ़ रहा होगा?"
- Ramesh asked, "Where will he be studying?"
- Ramesh asked where he would be studying.
- चाचा जी ने पूछा, "तुम क्या कर चुके होगे?"
- Uncle asked, "What will you have done?"
- Uncle asked what I would have done?
- मैंने पूछा, "वह चार घंटे से क्यों नहा रहा होगा?"
- I asked, "Why will he have been bathing from four hours?"
- I asked why he would have been bathing for four hours.
क्या से शुरू होने वाले वाक्यों के लिए
अगर आपने tense का अध्ययन किया है तो आपको मालूम होगा, जो वाक्य क्या से शुरू होते हैं उनमे 'क्या' शब्द को translate नहीं किया जाता है। जैसे- क्या आप जानते हैं? (do you know?)
Indirect speech में इन वाक्यों के पहले "if" लगाकर affirmative में बदल दिया जाता है और reporting verb में "ask" का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
- उसने कहा, "क्या तुम अकेले हो?"
- He asked, "Are you alone?"
- He asked if I was alone.
- पंकज ने पूछा, "क्या तुम अंग्रेजी बोल सकते हो?"
- Pankaj asked, "Can you speak English?"
- Pankaj asked if I could speak English.
- मैंने पूछा, "क्या तुम फ्री हो?"
- I asked, "Are you free?"
- I asked if he was free.
- उसने पूछा, "क्या वह उदास है?"
- He asked, "Is she sad?"
- He asked if she was sad.
- रमा ने कहा, "क्या सीरियल का समय हो गया है?"
- Rama asked, "Is it time for the serial?"
- Rama asked if that was time for the serial.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise
नीचे दिए गए वाक्यों से कंफ्यूज नहीं होना है। जैसे "I like pizza," she said और she said, "I like pizza." का अर्थ एक ही है। आप नीचे दिए गए वाक्यों को Indirect speech में बदलने का प्रयास करें।
- "I like pizza," she said.
- "Where is the nearest station?" he asked.
- "I will help you with your homework," she promised.
- "I can't come to the party tonight," he explained.
- "Please close the door," she said.
- "What time does the movie start?" he wondered.
- "Don't touch that!" she warned.
- "Let's go for a walk," he suggested.
- "I'm going to visit my grandmother tomorrow," she said.
- "Could you lend me your pen?" he asked.